Reduce Wastewater Production in the Home | WTE
Wastewater Production In The UK Home
In the UK, the average person produces 150 Litres of wastewater per day. This is far more than many of our European neighbours, (Denmark averages 80 litres) but far less than the USA, where the average is 370 litres/person/day. It is also 55% more water than we used in 1980.
93% of total water consumption is used indoors, and only 7% outdoors.
It is important to keep your water usage to within 150 litres/person/day, as this is the volume of water that is one of the main design criteria for sewage treatment plants.
Which Activities Produce the Most Wastewater?
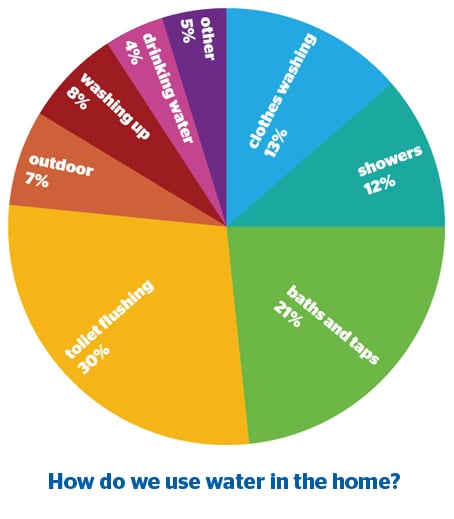
Toilets
As you can see from the chart, toilet flushes account for the most wastewater production.
The UK has over 45 million toilets which flush over 2 billion litres of wastewater down the drains every day (Waterwise). Of these toilets, over 7 million are the old, large cistern type and less than 20% are low water usage dual flush toilets.
Modern dual flush toilets use between 4 and 6 litres of water per flush but the old fashioned toilets use 13 litres every time you press the handle. As the average person flushes the toilet over 1500 times a year, an enormous volume of wastewater could be saved by changing to modern dual flush loos.
Another way of reducing the water used by older toilets is by filling a 2 litre plastic bottle with water and placing it in the cistern. By fitting these, we could save over 400 million litres of water and over 65 million Kg of CO2 per year.
Many Dual Flush toilets suffer from the problem of Leaking Valves, which increases the water consumption dramatically. You do not notice and cannot see the tiny stream of water, constantly running down the back of the pan. To check if your valve is still watertight, add some food colour to the water in the cistern and leave the toilet un-flushed for an hour. If colour is then found in the pan, it is time to replace the valve system.
Baths and Showers
It used to be thought that showers used less water than baths. Whilst this may have been true 20 years ago, nowadays, showering can use far more than bathing, due to the advent of Power Showers, Pressurised Hot Water Cylinders and the fact that as bathrooms have become warmer and more luxurious, people are spending much more time in the shower.
85% of home in the UK have at least one shower. An 8 minute shower, using a normal shower, uses 62 litres of water, but this can rise to 136 litres per shower if using a Power Shower or Pressurised Cylinder - almost your entire water allowance for 24 hours, if you have a sewage treatment plant or septic tank.
Modern power showers waste so much water, that a bath is much more eco-friendly.
Modern 1700mm long baths use 5 litres of water for every inch of water depth - with the person actually sitting in the bath. A 12" deep bath would use about the same amount of water as an 8 minute normal shower and many people don't have the bath water so high!
Every litre of this water has been treated to Drinking Water purity, so it makes sense to reduce this wastewater amount as much as we can.
Reducing Water Consumption In The Shower
- Reduce the amount of time you spend in the shower.
- Replace Power Showers with Low Flow or Aerated Showerhead showers. These give the same feeling but use only a fraction of the water.
- Turn the shower off whilst you wash and condition your hair.
Reducing Water Consumption In The Bath
- Reduce the depth of the bath water. Every inch saves 5 Litres.
- When replacing a bath, buy one that is no larger than the size you need. 'P' shaped baths use a lot more water for the same depth.
- Reuse bath water for washing cars, floors and watering the garden
Washing Clothes
Reducing Water Consumption for Laundry

- Buy a washing machine with a low water consumption. The water consumption is shown on the Energy Label on the machine. It is expressed in Litres used per year with average use.
- Buy a washing machine with a larger capacity. They don't use more water than smaller machines, but you can wash less often.
- Always ensure that you are washing a full load.
- Use the 'Lower Water Level' setting or 'Half Load' setting where possible.
Washing Up
Dishwashers are generally more common in larger households. A full dishwasher is more water efficient than hand washing, however, most dishwashers are rarely filled to maximum capacity.
The average dishwasher uses 13 litres per cycle, whereas washing up by hand uses 6 litres per minute, with the tap running and an average of 9 litres per washing-up bowl.
General
- Fix any dripping taps. A tap, dripping at 5 drips/minute wastes 1.5 litres of water/day.
- Only fill the kettle/bowl/bucket etc. with as much water as you actually need.
- Don't run the tap whilst you brush your teeth. Running taps use around 6 litres per minute.
- Always make sure that you run appliances on full loads.
- Check toilet valves for leaks
- Try to reduce the time spent in the shower. Go for a soak in the bath if you need to luxuriate.
